In this tutorial we will guide you through the steps of installing Odoo 11 on Ubuntu 16.04. We will also install Nginx web server and configure it as a reverse proxy. Odoo (formerly OpenERP) is simple and intuitive suite of open-source enterprise management applications such as Website Builder, eCommerce, CRM, Accounting, Manufacturing, Project and Warehouse Management, Human Resources, Marketing and many more. Used by more than 3.7 million users ranging from startups to large companies, it is one of the most popular software of this type in the world. Odoo comes in two editions, Community edition which is free and Enterprise edition. In our case we will install and use the Community edition of Odoo.
Prerequisites
– Ubuntu 16.04 VPS. We will use one of our SSD 2 VPS hosting plans.
– SSH access with root privileges
– PostgreSQL server
– Python version 3
– Nginx web server
Login via SSH and update the system
Login to your Ubuntu 16.04 VPS with SSH as user root
ssh root@IP_Address -p Port_number
Once you are logged in, run the following command to update all intalled packages to the latest available version
apt update && apt upgrade
If it is not already enabled, you can enable automatic updates on your Ubuntu 16.04 VPS.
Install PostgreSQL server

apt install -y postgresql
Once it is installed, enable the PostgreSQL server to start automatically upon server reboot
systemctl enable postgresql
Add repository and install Odoo
Odoo is not available in the official Ubuntu 16.04 repository, so in order to install it we will need to add the Odoo repository to the server. In order to do it, run the following commands
wget -O - https://nightly.odoo.com/odoo.key | apt-key add - echo "deb http://nightly.odoo.com/11.0/nightly/deb/ ./" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/odoo.list
Next, update the local package database
apt update
and install Odoo using the apt package manager
apt -y install odoo
This command will install Odoo, Python 3 and all necessary Python modules, create PostgreSQL user and start the Odoo instance. After the installation completes, you can check the status of the Odoo service:
systemctl status odoo
Output:
● odoo.service - Odoo Open Source ERP and CRM
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/odoo.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running)
Main PID: 7693 (odoo)
CGroup: /system.slice/odoo.service
└─7693 /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/odoo --config /etc/odoo/odoo.conf --logfile /var/log/odoo/odoo-server.log
After the installation is completed, edit Odoo’s configuration file and set the master admin password.
nano /etc/odoo/odoo.conf
Uncomment the ‘admin_passwrd’ line, and set a password as shown below
admin_passwd = MASTER_PASSWORD
where MASTER_PASSWORD is an actual strong password.
Restart the Odoo instance for the changes to take effect
systemctl restart odoo
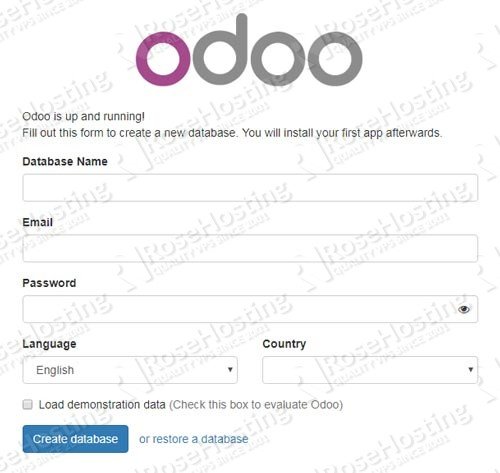
At this point you should be able to access Odoo using your server’s IP address. Open your favorite web browser and navigate to http://IP_Address:8069
Install Nginx web server and configure reverse proxy
In order to be able to access Odoo with a domain name, instead of typing the IP address and the port number, we need a web server. In this tutorial we will install and use Nginx. Run the following command to install it
apt -y install nginx
and enable it to start on server boot
systemctl enable nginx
Create Nginx server block for the domain name you will use for accessing Odoo. For example, we will use odoo.com
nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/odoo.com
upstream oddo {
server 127.0.0.1:8069;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name odoo.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/odoo.com.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/odoo.com.error.log;
proxy_buffers 16 64k;
proxy_buffer_size 128k;
location / {
proxy_pass http://oddo;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
}
location ~* /web/static/ {
proxy_cache_valid 200 60m;
proxy_buffering on;
expires 864000;
proxy_pass http://oddo;
}
}
Save the file and activate the Nginx block by creating a symbolic link
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/odoo.com /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/odoo.com
restart the web server for the changes to take effect
systemctl restart nginx
That’s all. If you closely followed the steps in this tutorial, you successfully installed Odoo 11 and configure Nginx as a reverse proxy. Now, you should be able to access Odoo with your domain name, create your first Odoo database using the master password we set earlier in this tutorial, and start working on your project.
For more information about Odoo 11, its features and configuration, please check their official documentation.

PS. If you enjoy reading this blog post on How to Install Odoo 11 on Ubuntu 16.04 with Nginx as a Reverse Proxy, feel free to share it on social networks using the shortcuts below, or simply leave a comment.
New version available here: How to Install Odoo 12 on Ubuntu 18.04 with Nginx as a Reverse Proxy.

Is there a reason to use “oddo” instead of “odoo” in the code? proxy_pass http://oddo
You can use any string for upstream in your configuration file.
Just you have to be careful to use unique string for every upstream on your server.