

In this tutorial, we will guide you through the steps of installing Odoo 12 on Ubuntu 18.04. We will also install Nginx and configure it as a reverse proxy. Odoo (formerly OpenERP) is a simple and intuitive suite of open-source enterprise management applications such as Website Builder, eCommerce, CRM, Accounting, Manufacturing, Project and Warehouse Management, Human Resources, Marketing, and many more. Odoo comes in two editions, the Community edition which is free, and the Enterprise edition. In our case, we will install and use the Community edition.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu 18.04 with 2GB of memory or higher
- Python 3
- PostgreSQL
- Nginx
- SSH access with root privileges
1. Log in via SSH and update the system
Log in to your Ubuntu 18.04 VPS with SSH as a root user
ssh root@IP_Address -p Port_number
You can check whether you have the proper Ubuntu version installed on your server with the following command:
# lsb_release -a
You should get this output:
Distributor ID: Ubuntu Description: Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS Release: 18.04 Codename: bionic
Once you are logged in, run the following command to update all installed packages to the latest available version.
apt update && apt upgrade
2. Install PostgreSQL server
Odoo requires a PostgreSQL database to store its information, so we will have to install the PostgreSQL server. We will install a PostgreSQL server using the following command:
apt install postgresql
Once installed, PostgreSQL server will be started and it’s also enabled to start at server boot.
3. Install Odoo
a. Method 1
If you want to install Odoo on your fresh server or you currently do not have an Odoo instance running on your server, you can follow this method.
Add repository and install Odoo
Odoo is not available in the official Ubuntu 18.04 repository, so in order to install it, we will need to add the Odoo repository to the server. In order to do it, run the following commands
wget -O - https://nightly.odoo.com/odoo.key | apt-key add - echo "deb http://nightly.odoo.com/12.0/nightly/deb/ ./" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/odoo.list
Next, update the local package database
apt update
and install Odoo using the apt package manager
apt install odoo
This command will install Odoo 12, Python 3 and all necessary Python modules, create PostgreSQL user and start the Odoo instance. After the installation is completed, you can check the status of the Odoo service:
systemctl status odoo
b. Method 2
If you want to run multiple Odoo version on your Ubuntu 18.04 server and/or you have another version of Odoo running on your server, you can follow these steps to install and configure Odoo 12 using their Github repository and Pyhton virtual environment.
Install dependencies
apt install build-essential wget git python3-pip python3-dev python3-venv python3-wheel python3-setuptools libxslt-dev libzip-dev libldap2-dev libsasl2-dev python3-setuptools node-less
Create a new system user for Odoo
useradd -m -d /opt/odoo12 -U -r -s /bin/bash odoo12
su - postgres -c "createuser -s odoo12"
Install Wkhtmltopdf
The wkhtmltopdf package is an open source tool that Odoo uses to make HTML in PDF formats so that it can print PDF reports. The recommended version for Odoo is 0.12.1 which is not available in the official Ubuntu 18.04 repositories.
cd /opt wget https://builds.wkhtmltopdf.org/0.12.1.3/wkhtmltox_0.12.1.3-1~bionic_amd64.deb apt install /opt/wkhtmltox_0.12.1.3-1~bionic_amd64.deb
That’s it, wkhtmltopdf has been installed.
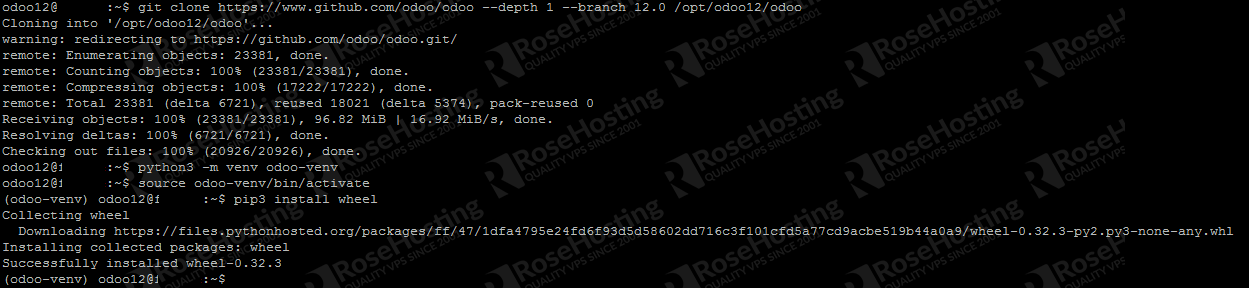
Install odoo 12
su - odoo12
git clone https://www.github.com/odoo/odoo --depth 1 --branch 12.0 /opt/odoo12/odoo
Now, still as user odoo12, let’s create a new python virtual environment
python3 -m venv odoo-venv
Then, let’s activate it
source odoo-venv/bin/activate
pip3 install wheel pip3 install -r odoo/requirements.txt
(venv) $ deactivate && exit
We need an Odoo configuration file, we can copy the one from GitHub:
cp /opt/odoo12/odoo/debian/odoo.conf /etc/odoo12.conf
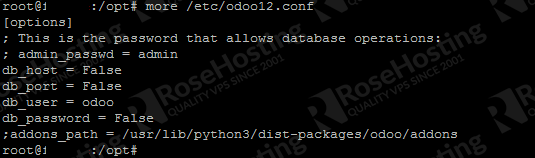
We can create a master password, you can change the “m0d1fyth15” to your own password. Also, add addons_path and xmlrpc_port if you want to specify a port to run Odoo on, if you do not specify it, then Odoo will run on its default port, 8069.
nano /etc/odoo12.conf
[options] ; This is the password that allows database operations: admin_passwd = m0d1fyth15 db_host = False db_port = False db_user = odoo12 db_password = False addons_path = /opt/odoo12/odoo/addons xmlrpc_port = 8001
Save the file then exit, then we create a systemd file to run Odoo 12.
nano /etc/systemd/system/odoo12.service
[Unit] Description=Odoo12 Requires=postgresql.service After=network.target postgresql.service [Service] Type=simple SyslogIdentifier=odoo12 PermissionsStartOnly=true User=odoo12 Group=odoo12 ExecStart=/opt/odoo12/odoo-venv/bin/python3 /opt/odoo12/odoo/odoo-bin -c /etc/odoo12.conf StandardOutput=journal+console [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start odoo12
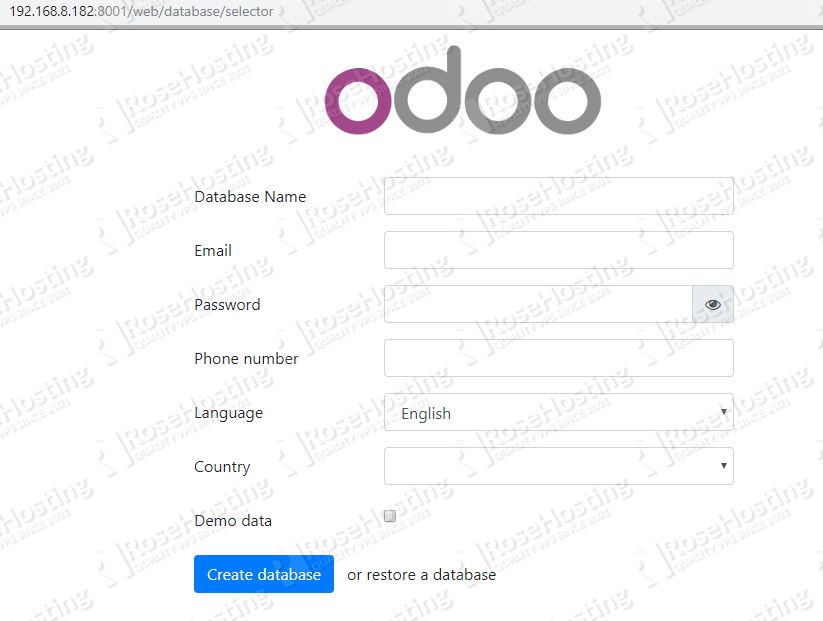
At this point, we can access our new Odoo 12 installation at http://IP_Address:Odoo_port. To access it using a domain we need to configure a reverse proxy, and this time we will use nginx to do it.
Install Nginx web server and configure reverse proxy
In order to be able to access Odoo with a domain name, instead of typing the IP address and the port number, we need a web server. In this tutorial we will install and use Nginx. Run the following command to install it
apt -y install nginx
and enable it to start on server boot
systemctl enable nginx
Create Nginx server block for the domain name you will use for accessing Odoo. For example, we will use yourdomain.com
nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/yourdomain.com
upstream odoo12 {
server 127.0.0.1:8069;
}
server {
listen 80 default;
server_name yourdomain.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/odoo.com.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/odoo.com.error.log;
proxy_buffers 16 64k;
proxy_buffer_size 128k;
location / {
proxy_pass http://odoo12;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
}
location ~* /web/static/ {
proxy_cache_valid 200 60m;
proxy_buffering on;
expires 864000;
proxy_pass http://odoo12;
}
}
Save the file and activate the Nginx block by creating a symbolic link
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/yourdomain.com /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/yourdomain.com
restart the web server for the changes to take effect
systemctl restart nginx
Now you should be able to access Odoo with your domain name at http://yourdomain.com, create your first Odoo database using the master password we set earlier in this tutorial, and start working on your project. For more information about Odoo 12, its features and configuration, please check their official documentation.

Of course, you don’t have to install Odoo 12 on Ubuntu 18.04 if you use one of our Odoo VPS Hosting services, in which case you can simply ask our expert Linux admins to install Odoo 12 on Ubuntu 18.04, for you. They are available 24×7 and will take care of your request immediately.
PS. If you liked this post, on installing Odoo 12 on Ubuntu 18.04 with Apache as a reverse proxy, please share it with your friends on the social networks using the buttons below or simply leave a comment in the comments section. Thanks.
thanks alot, very useful info