Jenkins is an open source extensible automation server which can be used as a simple CI server (Continuous Integration) or as a CD hub (Continuous Delivery). In this tutorial we are going to show you how to install Jenkins on a Linux VPS running Debian 9 as an operating system.
Prerequsites
In order to run Jenkins on your server, you need to have Java installed. If you don’t have Java installed, you can check our tutorial about how to install Java on Debian 9. Also you need to have root access to the server or system user with sudo privileges.
Jenkins can be used to automate all sorts of tasks, from building and testing to developing and deploying software. Its functionality can be extended through hundreds of plugins while you can configure it via its web interface.
Jenkins runs on different platforms and operating systems. On a Debian 9 VPS it can be easily installed through the apt package manager.
Install Jenkins on a Debian 9 VPS
To install Jenkins on your server running Debian 9 as an operating system, you need to have root access to it. If you have root access to the server, you should connect to the server via SSH and update the already installed software to the latest version by using the following commands:
apt-get update apt-get upgrade
This will update the package index and will update the software to the latest version available.
Next, we will be installing stable LTS version of Jenkins so we should add the appropriate repository. Run the following commands to do so:
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add - sh -c 'echo deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list'
Once you add the repository update the package index once again:
apt-get update
Finally, install Jenkins by running the command below:
apt-get install jenkins
If you get the following error while installing Jenkins:
host jenkins[2747]: ERROR: No Java executable found in current PATH: /bin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/usr/sbin host jenkins[2747]: If you actually have java installed on the system make sure the executable is in the aforementioned path and that 'type -p java' returns the java executable path host systemd[1]: jenkins.service: Control process exited, code=exited status=1
It means you don’t have Java installed on your Debian VPS. Go back to the prerequisites section for instructions on how to install Java on your machine.
Manage Jenkins on Debian 9
Now that the installation of Jenkins is completed, it is good to know how you can manage the Jenkins service. To start the Jenkins service, run the following command in the terminal:
systemctl start jenkins.service
To stop the Jenkins service, you can use the following command:
systemctl stop jenkins.service
To restart the service, you can run the following command:
systemctl restart jenkins.service
To check the status of the Jenkins service, run the following command:
systemctl status jenkins.service
If Jenkins is up and running on your Linux VPS at the moment, the output will be similar to the one below:
# systemctl status jenkins.service
● jenkins.service - LSB: Start Jenkins at boot time
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/jenkins; generated; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Mon 2018-09-10 11:24:25 CDT; 2min 35s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
To enable the Jenkins service on system boot, run the following command:
systemctl enable jenkins.service
In case you want Jenkins disabled on system boot, run the following command:
systemctl disable jenkins.service
Access and Configure Jenkins on Debian 9
Jenkins by default listens on port 8080. If you have another service listening on that port, Jenkins will fail to start. In that case you need to edit the /etc/default/jenkins file.
Replace the line
----HTTP_PORT=8080----
with
----HTTP_PORT=8081----
Where 8081 is the number of the port where you want Jenkins to listen to. Then restart Jenkins.
systemctl restart jenkins.service
Now open your favorite web browser and access the Jenkins web interface by typing your server IP address followed by the port number in the search bar. The page will be similar to the one below.
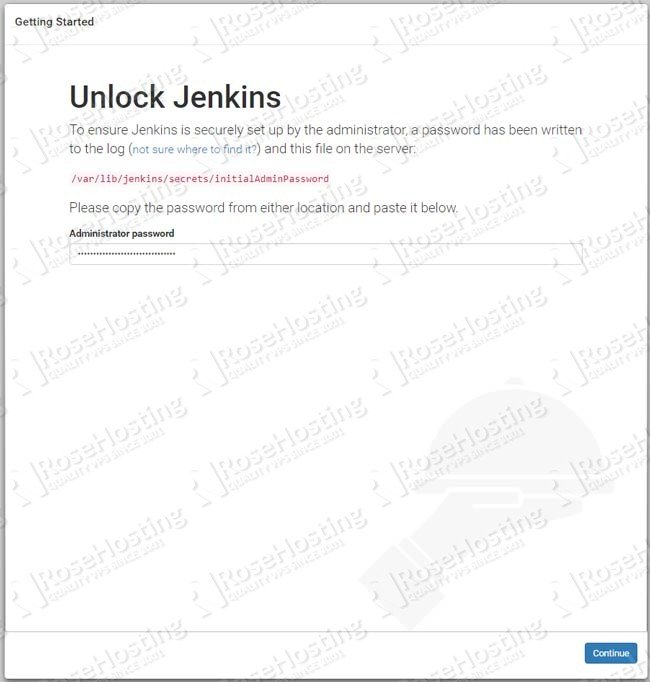
If this is what you are seeing on your screen, it means you need to unlock Jenkins. You can find the password to unlock Jenkins in the /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword file.
cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
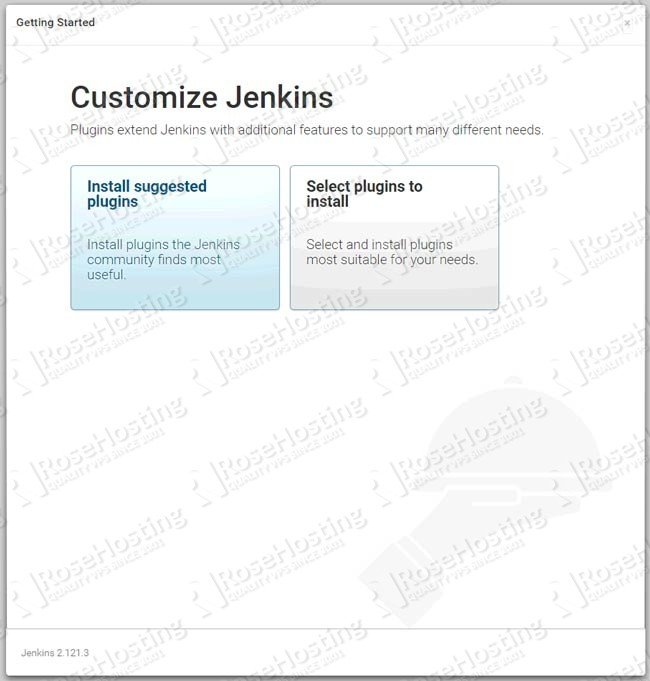
Enter the password and click on Continue. You can now continue and install the plugins needed for your projects.
A good starting point is to read the Jenkins user documentation where you can find many instructions and usage examples.

PS. If you liked this post on how to install Jenkins on Debian 9, please share it with your friends on the social networks using the buttons on the left or simply leave a reply below. Thanks.