Mastodon is an open-source free social network based on open web protocol. It used Ruby on Rails for the back-end and React.js and Redux for the front-end. In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Mastodon on a CentOS 7 server.
Table of Contents
1. Update your CentOS 7 server and install the necessary packages
Log in to your VPS via SSH as a sudo user:
ssh userame@IP_Address
Once you are logged in, issue the following commands to make sure all installed packages are up to date:
sudo yum update
Next, install the install the pre-requisite packages necessary for building Mastodon with the following command:
sudo yum install curl git gpg gcc git-core zlib zlib-devel gcc-c++ patch readline readline-devel libyaml-devel libffi-devel openssl-devel make autoconf automake libtool bison curl sqlite-devel ImageMagick libxml2-devel libxslt-devel gdbm-devel ncurses-devel glibc-headers glibc-devel libicu-devel libidn-devel protobuf-devel protobuf
2. Install Node.js and Yarn
We will install Node.js v8 LTS from the NodeSource repository which depends on the EPEL repository being enabled.
To enable the EPEL repository on your CentOS 7 VPS, issue the following command:
sudo yum install epel-release curl
Once the EPEL repository is enabled run the following command to add the Node.js v8 LTS repository:
curl --silent --location https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_8.x | sudo bash -
Once the NodeSource repository is enabled install the Node.js with the following command:
sudo yum install nodejs
Enable the Yarn RPM repository with:
curl --silent --location https://dl.yarnpkg.com/rpm/yarn.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/yarn.repo
Install the latest Yarn version with:
sudo yum install yarn
3. Install PostgreSQL
Enable the PostgreSQL repository:
sudo rpm -Uvh https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/9.6/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgdg-centos96-9.6-3.noarch.rpm
To install the PostgreSQL server run the following command:
sudo yum install postgresql96-server postgresql96-contrib postgresql96-devel
Once the installation is completed, create a new database cluster with:
sudo /usr/pgsql-9.6/bin/postgresql96-setup initdb
Start the PostgreSQL service and enable it to start on boot:
sudo systemctl enable postgresql-9.6 sudo systemctl start postgresql-9.6
Login to the PostgreSQL shell:
sudo -u postgres psql
Create a new user for the Mastodon instance:
CREATE USER mastodon CREATEDB;
4. Install Redis
Installing Redis is pretty straightforward, just run the following command:
sudo yum install redis
5. Create a new system user
To create a new system user for Mastodon run the following command:
sudo adduser mastodon
6. Install Ruby
We will install Ruby using the Rbenv script.
Before cloning the rbenv repository switch to the new mastodon user:
sudo su - mastodon
Set up rbenv and ruby-build with the following commands:
cd git clone git://github.com/sstephenson/rbenv.git .rbenv echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.rbenv/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bash_profile echo 'eval "$(rbenv init -)"' >> ~/.bash_profile exec $SHELL git clone git://github.com/sstephenson/ruby-build.git ~/.rbenv/plugins/ruby-build echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.rbenv/plugins/ruby-build/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bash_profile exec $SHELL
Once both rbenv and ruby-build are setups, install the latest Ruby version with”
rbenv install 2.5.1 rbenv global 2.5.1
To verify everything is done correctly, use the command ruby --version.
The output should be similar to the following:
ruby --version ruby 2.5.1p57 (2018-03-29 revision 63029) [x86_64-linux]
7. Clone the Mastodon git repository and install dependencies
The following commands are also run as mastodon user.
Clone the mastodon git repository into the ~/live directory and checkout to the latest stable Mastodon branch:
cd git clone https://github.com/tootsuite/mastodon.git live cd ~/live git checkout $(git tag -l | grep -v 'rc[0-9]*$' | sort -V | tail -n 1)
Install bundler and ruby dependencies with the following commands:
gem install bundler bundle install -j$(getconf _NPROCESSORS_ONLN) --deployment --without development test
Install the node.js dependencies with:
yarn install --pure-lockfile
8. Configure Mastodon
The following commands are run as mastodon user.
Change to the Mastodon installation directory and run the following command to start the setup:
cd ~/live RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake mastodon:setup
The installer will ask you several questions, generate new app secret, set up the database schema and compile the assets.
Your instance is identified by its domain name. Changing it afterward will break things. Domain name: your-domain.com Single user mode disables registrations and redirects the landing page to your public profile. Do you want to enable single user mode? No Are you using Docker to run Mastodon? no PostgreSQL host: /var/run/postgresql PostgreSQL port: 5432 Name of PostgreSQL database: mastodon_production Name of PostgreSQL user: mastodon Password of PostgreSQL user: Database configuration works! 🎆 Redis host: localhost Redis port: 6379 Redis password: Redis configuration works! 🎆 Do you want to store uploaded files on the cloud? No Do you want to send e-mails from localhost? yes E-mail address to send e-mails "from": Mastodon <notifications@your-domain.com> Send a test e-mail with this configuration right now? no This configuration will be written to .env.production Save configuration? Yes Now that configuration is saved, the database schema must be loaded. If the database already exists, this will erase its contents. Prepare the database now? Yes Running `RAILS_ENV=production rails db:setup` ... Created database 'mastodon_production' ... Done! The final step is compiling CSS/JS assets. This may take a while and consume a lot of RAM. Compile the assets now? Yes Running `RAILS_ENV=production rails assets:precompile` ... yarn install v1.9.4 ... Using /home/mastodon/live/config/webpacker.yml file for setting up webpack paths Compiling… Compiled all packs in /home/mastodon/live/public/packs Rendering errors/500.html.haml within layouts/error Rendered errors/500.html.haml within layouts/error (2596.9ms) Done! All done! You can now power on the Mastodon server 🐘 Do you want to create an admin user straight away? Yes Username: admin E-mail: admin@your-domain.com You can login with the password: 80b4aA233adaeS86d095Scbf79302f81 You can change your password once you login.
9. Create Mastodon systemd units
The following commands are run as root or sudo user.
Open your text editor and create the following systemd unit files:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/mastodon-web.service
[Unit] Description=mastodon-web After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=mastodon WorkingDirectory=/home/mastodon/live Environment="RAILS_ENV=production" Environment="PORT=3000" ExecStart=/home/mastodon/.rbenv/shims/bundle exec puma -C config/puma.rb ExecReload=/bin/kill -SIGUSR1 $MAINPID TimeoutSec=15 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/mastodon-sidekiq.service
[Unit] Description=mastodon-sidekiq After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=mastodon WorkingDirectory=/home/mastodon/live Environment="RAILS_ENV=production" Environment="DB_POOL=5" ExecStart=/home/mastodon/.rbenv/shims/bundle exec sidekiq -c 5 -q default -q push -q mailers -q pull TimeoutSec=15 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/mastodon-streaming.service
[Unit] Description=mastodon-streaming After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=mastodon WorkingDirectory=/home/mastodon/live Environment="NODE_ENV=production" Environment="PORT=4000" ExecStart=/usr/bin/npm run start TimeoutSec=15 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Enable and start all services:
sudo systemctl enable mastodon-web.service sudo systemctl enable mastodon-sidekiq.service sudo systemctl enable mastodon-streaming.service sudo systemctl start mastodon-web.service sudo systemctl start mastodon-sidekiq.service sudo systemctl start mastodon-streaming.service
10. Install and configure Nginx
To install Nginx run the following command:
sudo yum install nginx
Once nginx is installed, create a server block for your domain. Do not forget to set the correct path to the SSL certificate and private key.
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/your-domain.com.conf
map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade {
default upgrade;
'' close;
}
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name your-domain.com;
root /home/mastodon/live/public;
# Useful for Let's Encrypt
location /.well-known/acme-challenge/ { allow all; }
location / { return 301 https://$host$request_uri; }
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name your-domain.com;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!MEDIUM:!LOW:!aNULL:!NULL:!SHA;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/certificate.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/certificate.key;
keepalive_timeout 70;
sendfile on;
client_max_body_size 80m;
root /home/mastodon/live/public;
gzip on;
gzip_disable "msie6";
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_buffers 16 8k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000";
location / {
try_files $uri @proxy;
}
location ~ ^/(emoji|packs|system/accounts/avatars|system/media_attachments/files) {
add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=31536000, immutable";
try_files $uri @proxy;
}
location /sw.js {
add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=0";
try_files $uri @proxy;
}
location @proxy {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
proxy_set_header Proxy "";
proxy_pass_header Server;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3000;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
tcp_nodelay on;
}
location /api/v1/streaming {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
proxy_set_header Proxy "";
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:4000;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
tcp_nodelay on;
}
error_page 500 501 502 503 504 /500.html;
}
Save the file and restart the nginx service:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
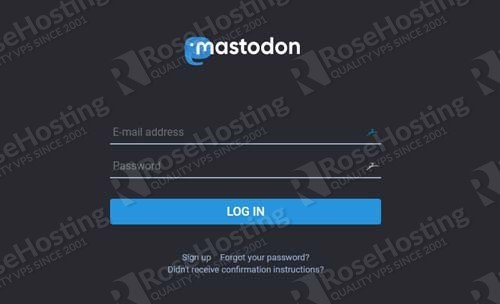
You can now open your browser, type your domain and you will be presented with the Mastodon login form.

PS. If you liked this post, on How to Install Mastodon on CentOS 7 please share it with your friends on the social networks using the buttons on the left or simply leave a reply below. Thanks.

hi there,
i did follow the guide which was helpful thank you. I have a problem, UI doesnt look anything like the screenshot . it looks like some distorted mobile site. how do I fix that?
Side note: rbenv install 2.5.1 wont work when u run bundler tasks it requests version 2.6.1, then it . works