In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Redmine on an Ubuntu 18.04 VPS.

Table of Contents
Prerequisites:
- A registered domain name pointing to your server IP address. In this tutorial, we will use
your_domain.com. (optional) - Full SSH root access or a user with sudo privileges.
- SSL certificate installed for your domain. In our tutorial we will use a free Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate. (optional)
Step 1: Connect to your Server
To connect to your server via SSH as the root user, use the following command:
$ ssh root@IP_ADDRESS -p PORT_NUMBER
and replace “IP_ADDRESS” and “PORT_NUMBER” with your actual server IP address and SSH port number.
Once logged in, make sure that your server is up-to-date by running the following commands:
$ apt-get update $ apt-get upgrade
Step 2: Install MySQL
Next, we need to install the MySQL server. Ubuntu 18.04 has the latest stable version of MySQL ready for installation through the pre-installed repositories.
The following command will install the latest MySQL 5.7 server from the official Ubuntu repositories:
$ apt-get install mysql-server
The MySQL web server will be started automatically as soon as the installation is completed.
You can also enable the MySQL service to automatically start up upon server reboot with the following command:
$ systemctl enable mysql
Run the following command to further secure your installation:
$ mysql_secure_installation
This script will help you to perform important security tasks like setting up a root password, disable remote root login, remove anonymous users, etc. If the script asks for the root password, just press the [Enter] key, as no root password is set by default.
Step 3: Create a Database for Redmine
Next, we need to create a database for our Redmine installation. Log in to your MySQL server with the following command and enter your MySQL root password:
$ mysql -uroot -p
In this section, we will create a new MySQL database:
CREATE DATABASE redmine_db;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON redmine_db.* TO 'redmine_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Password';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
exit;
Make sure to replace the password “Password” with a real, strong password.
Step 4: Install Ruby
The easiest way to install Ruby on your Ubuntu 18.04 server is through the apt package manager. The current version in the Ubuntu repositories is 2.5.1 which is the latest stable version of Ruby at the time of writing this tutorial.
Install Ruby with the following command:
$ apt-get install ruby-full
To verify everything is done correctly, use the command ruby --version.
The output should be similar to the following:
$ ruby --version ruby 2.5.1p57 (2018-03-29 revision 63029) [x86_64-linux-gnu]
Step 5: Install Nginx and Passenger
To install Nginx on your Ubuntu 18.04 server, you need to enter the following command:
$ apt-get install nginx
Enable Nginx to start on boot and start the service using these two lines:
$ systemctl start nginx $ systemctl enable nginx
To install Passenger, an Nginx module, start by installing the necessary package prerequisites:
$ apt-get install dirmngr gnupg apt-transport-https ca-certificates
Import the repository GPG key and enable the “Phusionpassenger” repository:
$ apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 561F9B9CAC40B2F7 $ add-apt-repository 'deb https://oss-binaries.phusionpassenger.com/apt/passenger bionic main'
Once the repository is enabled, update the packages list and install the Passenger Nginx module with:
$ apt-get update $ apt-get install libnginx-mod-http-passenger
Step 6: Download and Install Redmine
We need to install the dependencies necessary to build Redmine:
$ apt-get install build-essential libmysqlclient-dev imagemagick libmagickwand-dev
Go to Redmine’s official website and download the latest stable release of the application. At the time of this article being published, the latest version of Redmine is version 4.0.2.
$ wget https://www.redmine.org/releases/redmine-4.0.2.zip -o /opt/redmine.zip
Once the tar.gz archive is downloaded, unpack it to the /opt directory on your server:
$ cd /opt $ unzip redmine.zip $ mv redmine-4.0.2 /opt/redmine
Now apply the following required file and folder permissions (these are needed in order for Nginx to have access to the files):
$ chown -R www-data:www-data /opt/redmine/ $ chmod -R 755 /opt/redmine/
Configure database settings:
$ cd /opt/redmine/config/ $ cp configuration.yml.example configuration.yml $ cp database.yml.example database.yml
Open the database.yml file using your preferred text editor and update the username/password details based on the ones you set in Step 3:
$ nano database.yml
production: adapter: mysql2 database: redmine_db host: localhost username: redmine_user password: "Password" encoding: utf8
Then save and exit the file.
Step 7: Install Ruby Dependencies, Generate Keys, and Migrate the Database
Navigate to the Redmine directory and install bundler and other Ruby dependencies:
$ cd /opt/redmine/
$ gem install bundler --no-rdoc --no-ri
$ bundle install --without development test postgresql sqlite
Run the following command to generate the keys and migrate the database:
$ bundle exec rake generate_secret_token $ RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake db:migrate
Step 8: Configure Nginx
Open your preferred text editor and create the following Nginx server block file:
$ nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/your_domain.com.conf
# Redirect HTTP -> HTTPS
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.your_domain.com your_domain.com;
include snippets/letsencrypt.conf;
return 301 https://your_domain.com$request_uri;
}
# Redirect WWW -> NON WWW
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name www.your_domain.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain.com/chain.pem;
include snippets/ssl.conf;
return 301 https://your_domain.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name your_domain.com;
root /opt/redmine/public;
# SSL parameters
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain.com/chain.pem;
include snippets/ssl.conf;
include snippets/letsencrypt.conf;
# log files
access_log /var/log/nginx/your_domain.com.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/your_domain.com.error.log;
passenger_enabled on;
passenger_min_instances 1;
client_max_body_size 10m;
}
Then save and exit the file.
To enable the server configuration that we just created, run the following command:
$ ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/your_domain.com.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/your_domain.com.conf
Now, check the config file to make sure that there are no syntax errors. Any errors could crash the web server on restart.
$ nginx -t
Output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
If there are no errors, you can reload the Nginx config.
$ service nginx reload
Step 9: Access Redmine
Finally, you can start your browser and the installation is successful, a screen similar to the following will appear when you access https://your_domain.com/:
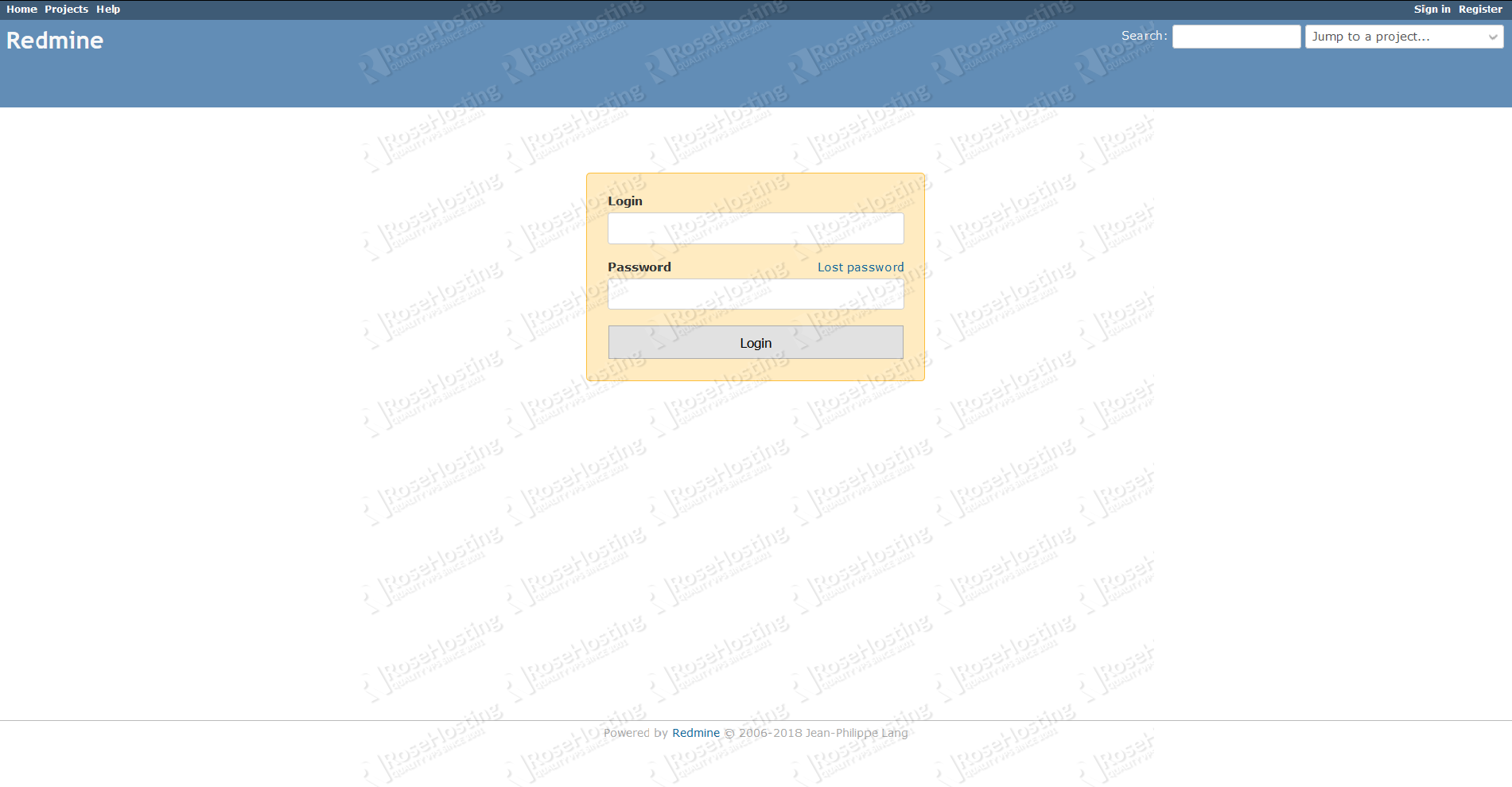
The default login credentials for Redmine are:
- Username: admin
- Password: admin
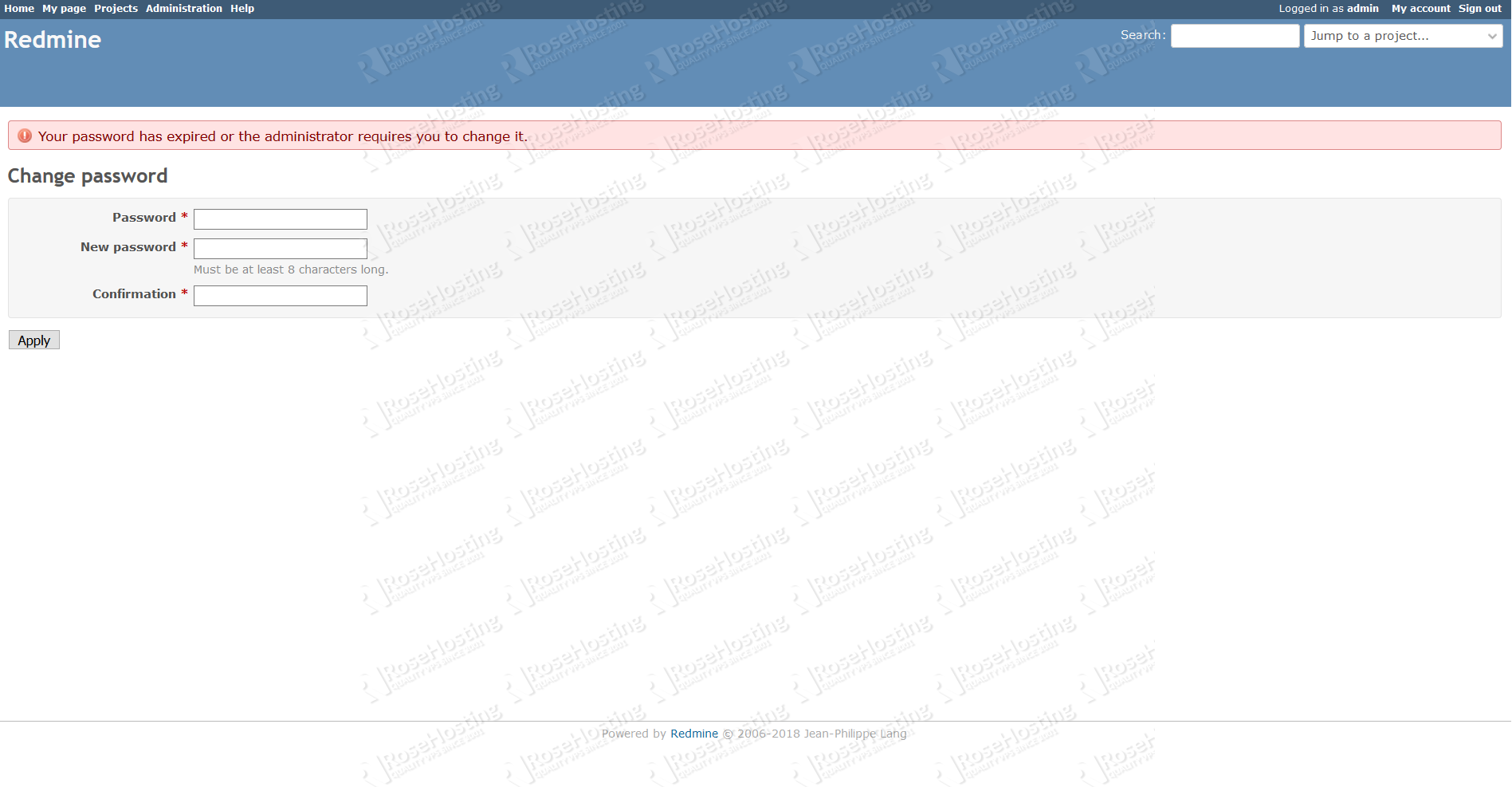
Once you change the password you will be redirected to the admin account page.
That’s it. You have successfully installed Redmine on your Ubuntu 18.04 VPS.

PS. If you liked this post on how to install Redmine on Ubuntu 18.04, please share it with your friends on the social networks using the buttons below, or simply leave a reply down in the comments section. Thank you.

I’m having trouble getting through the database migration…
$ sudo RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake db:migrate
rake aborted!
Sprockets::Railtie::ManifestNeededError: Expected to find a manifest file in `app/assets/config/manifest.js`
But did not, please create this file and use it to link any assets that need
to be rendered by your app:
Example:
//= link_tree ../images
//= link_directory ../javascripts .js
//= link_directory ../stylesheets .css
and restart your server
/var/lib/gems/2.5.0/gems/sprockets-rails-3.2.1/lib/sprockets/railtie.rb:105:in `block in ‘
/var/lib/gems/2.5.0/gems/railties-5.2.2/lib/rails/initializable.rb:32:in `instance_exec’
/var/lib/gems/2.5.0/gems/railties-5.2.2/lib/rails/initializable.rb:32:in `run’
/var/lib/gems/2.5.0/gems/railties-5.2.2/lib/rails/initializable.rb:61:in `block in run_initializers’
/var/lib/gems/2.5.0/gems/railties-5.2.2/lib/rails/initializable.rb:60:in `run_initializers’
/var/lib/gems/2.5.0/gems/railties-5.2.2/lib/rails/application.rb:361:in `initialize!’
/opt/redmine/config/environment.rb:14:in `’
/var/lib/gems/2.5.0/gems/railties-5.2.2/lib/rails/application.rb:337:in `require’
/var/lib/gems/2.5.0/gems/railties-5.2.2/lib/rails/application.rb:337:in `require_environment!’
/var/lib/gems/2.5.0/gems/railties-5.2.2/lib/rails/application.rb:520:in `block in run_tasks_blocks’
/var/lib/gems/2.5.0/gems/rake-13.0.1/exe/rake:27:in `’
Tasks: TOP => db:migrate => db:load_config => environment
(See full trace by running task with –trace)
try with this first: mkdir -p app/assets/config && echo ‘{}’ > app/assets/config/manifest.js
You will not be able to install SSL certificate and configure the same Nginx setup, it will not work properly if you just change yourdomain.com with localhost, it is a different setup
With new version or redmine 4.1.1 there is problem installing pg dependency via gem.
You need to install libpq-dev`apt-get install libpq-dev`