

Table of Contents
1. Installing Linux Screen Command
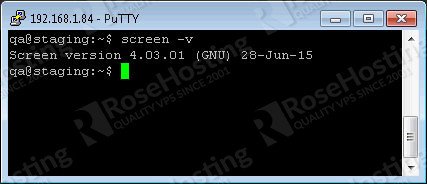
The screen comes preinstalled on some of the popular distributions. You can check if it is installed on your server using the following command
screen -v
If you do not have a screen to the VPS, you can easily install it using the package manager provided by the OS.
2. Install Linux Screen Command – CentOS/RedHat/Fedora
yum -y install screen
- Ubuntu/Debian
apt-get -y install screen
3. How to start a Linux Screen Command session
You can start screen by typing ‘screen’ at the command prompt and a new screen session will be started which looks the same as the command prompt
screen
It is a good practice to start screen sessions with descriptive names so you can easily remember which process is running in the session. To create a new session with a session name run the following command
screen -S name
and replace ‘name’ with a meaningful name for your session.
4. Detach from Linux Screen Command Session
To detach from the current screen session you can press ‘Ctrl-A‘ and ‘d‘ on your keyboard. All screen sessions will still be active and you can re-attach to them at any time later.
5. Reattach to Linux Screen Command
If you have detached from a session or your connection is interrupted for some reason, you can easily re-attach by executing the following command:
screen -r
If you have multiple screen sessions you can list them with ‘ls’
screen -ls There are screens on: 7880.session (Detached) 7934.session2 (Detached) 7907.session1 (Detached) 3 Sockets in /var/run/screen/S-root.
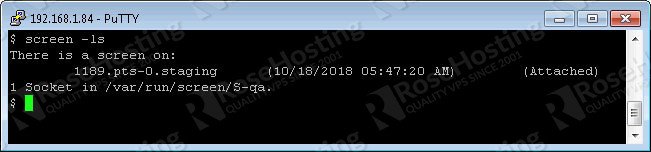
In our example, we have three active screen sessions. So, if you want to restore the session ‘session2’ you can execute
screen -r 7934
or you can use the screen name
screen -r -S session2
6. Terminate Linux Screen Command Session
There are several ways to terminate the screen session. You can do it by pressing ‘Ctrl‘ + ‘d‘ on your keyboard or use the ‘exit’ command line command.
To see all the useful features of the screen command you can check the screen’s man page.
man screen NAME screen - screen manager with VT100/ANSI terminal emulation SYNOPSIS screen [ -options ] [ cmd [ args ] ] screen -r [[pid.]tty[.host]] screen -r sessionowner/[[pid.]tty[.host]]

PS. If you liked this post on how to use the Linux Screen Command, please share it with your friends on the social networks using the buttons below or simply leave a comment in the comment section. Thanks.
Good explanation.