In this tutorial, we will install Drupal CMS on Debian 11 OS.
Drupal is a free, open-source content management system written in PHP. It offers a variety of modules, themes, localization in 100 different languages, auto-update notifications, etc. The Drupal community is getting bigger daily, reaching 1.4 million members, including actively contributing users. The advantage of using Drupal is that it is compatible with any system that has PHP and a database for storing Drupal data.
In this blog post, we will install Drupal on Debian 11 with the LAMP stack, which may take up to 20 minutes. Let’s get things working!
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
- A server with Debian 11 as OS
- User privileges: root or non-root user with sudo privileges
Step 1. Update the System
Update the system packages to the latest versions available. Execute the following command:
sudo apt-get update -y && sudo apt-get upgrade -y
Step 2. Install LAMP Stack
First, we will install the Apache Web server. Execute the following command:
sudo apt-get install apache2 -y
Once installed, start and enable the service.
sudo systemctl enable apache2 && sudo systemctl start apache2
Check if the service is up and running:
sudo systemctl status apache2
You should receive the following output:
root@host:~# sudo systemctl status apache2 ● apache2.service - The Apache HTTP Server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/apache2.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2022-12-27 06:38:17 CST; 36min ago Docs: https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/ Main PID: 423 (apache2) Tasks: 55 (limit: 4675) Memory: 18.2M CPU: 510ms CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service ├─423 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start ├─445 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start └─446 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start Dec 27 06:38:17 host.test.vps systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server... Dec 27 06:38:17 host.test.vps systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server.
Next, we will install PHP along with its extensions. To do that, first, add the GPG key and the repo with the following commands:
apt -y install lsb-release apt-transport-https ca-certificates wget -O /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/php.gpg https://packages.sury.org/php/apt.gpg echo "deb https://packages.sury.org/php/ $(lsb_release -sc) main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/php.list sudo apt-get update -y
Once the PHP key and repo are added, you can install the PHP with extensions using this long command:
sudo apt-get install php8.2 php8.2-common php8.2-curl libapache2-mod-php php8.2-imap php8.2-redis php8.2-cli php8.2-snmp php8.2-xml php8.2-zip php8.2-mbstring php-gd php-xml php-mysql php-mbstring -y
After successful installation, you can check the PHP version with the following command:
php -v
You should get the following output:
root@host:~# php -v PHP 8.1.13 (cli) (built: Nov 26 2022 14:27:02) (NTS) Copyright (c) The PHP Group Zend Engine v4.1.13, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v8.1.13, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
The last of the LAMP stack is the MariaDB database service. To install it execute the following command:
sudo apt-get install mariadb-server -y
Start and enable the mariadb.service with the following commands:
sudo systemctl start mariadb && sudo systemctl enable mariadb
Check the status of the mariadb.service
sudo systemctl status mariadb
You should receive the following output:
root@host:~# sudo systemctl status mariadb ● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.5.18 database server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2022-12-27 07:45:16 CST; 5min ago Docs: man:mariadbd(8) https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/ Main PID: 43791 (mariadbd) Status: "Taking your SQL requests now..." Tasks: 8 (limit: 4675) Memory: 78.0M CPU: 606ms CGroup: /system.slice/mariadb.service └─43791 /usr/sbin/mariadbd
Now, when the LAMP stack is installed, we are ready to proceed with database creation and Drupal installation.
Step 3. Create a Drupal Database and User
To create a Drupal database, the Drupal user and grant the permissions for that user to the database first log in to MySQL command line with the mysql command and execute the following lines of code one by one:
CREATE USER 'drupal'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'YourStrongPasswordHere'; CREATE DATABASE drupal; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON drupal.* TO 'drupal'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
Now, the database and user with the name drupal have been added with proper permissions. We are ready to download the Drupal installation and set the file and folder permissions.
Step 4. Download Drupal
First, go into the Document root of the Apache web server:
cd /var/www/html
To download the latest stable release of Drupal 10, execute the following command:
wget https://ftp.drupal.org/files/projects/drupal-10.0.0.zip unzip drupal-10.0.0.zip mv drupal-10.0.0/ drupal/ rm drupal-10.0.0.zip
Set the right permissions to files and folders.
chown -R www-data:www-data drupal/
find . -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
find . -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
In the next step, we will configure the Apache Virtual Host file.
Step 5. Create Apache Virtual Host File
Go into the Apache directory and create a configuration file for the Drupal CMS.
cd /etc/apache2/sites-available/ touch drupal.conf
Open the file, paste the following lines of code, save it, and close it.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName yourdomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/drupal
<Directory /var/www/html/drupal>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Enable the Apache configuration for Drupal and rewrite module.
a2dissite 000-default.conf sudo a2enmod rewrite sudo a2ensite drupal.conf
Check the syntax:
apachectl -t
You should receive the following output:
root@vps:~# apachectl -t Syntax OK
If the syntax is OK, restartd the Apache service.
systemctl restart apache2
Once the Apache service is restarted, you can finish the Drupal installation at http://yourdomain.com
Step 6. Finish Drupal Installation
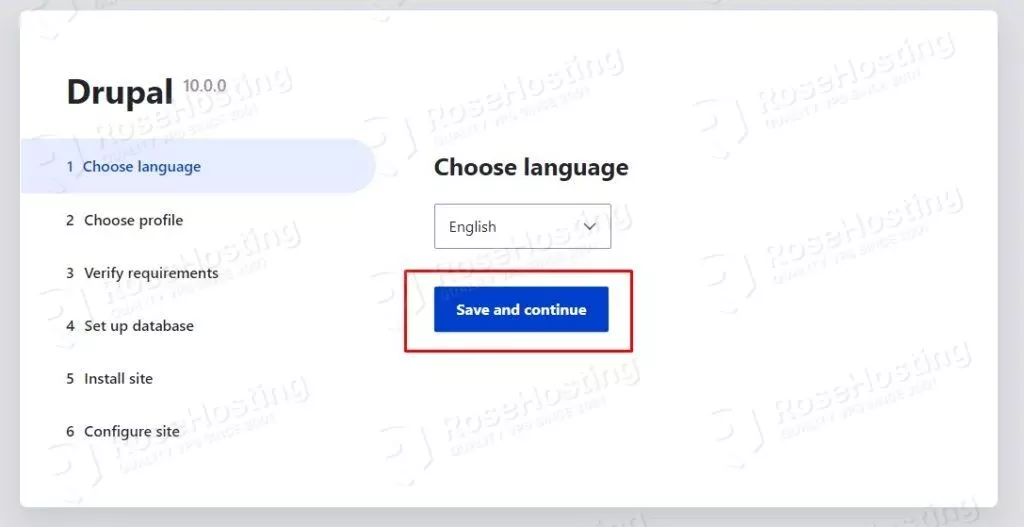
The installation can be finished at http://yourdomain.com. You should see the following screen:
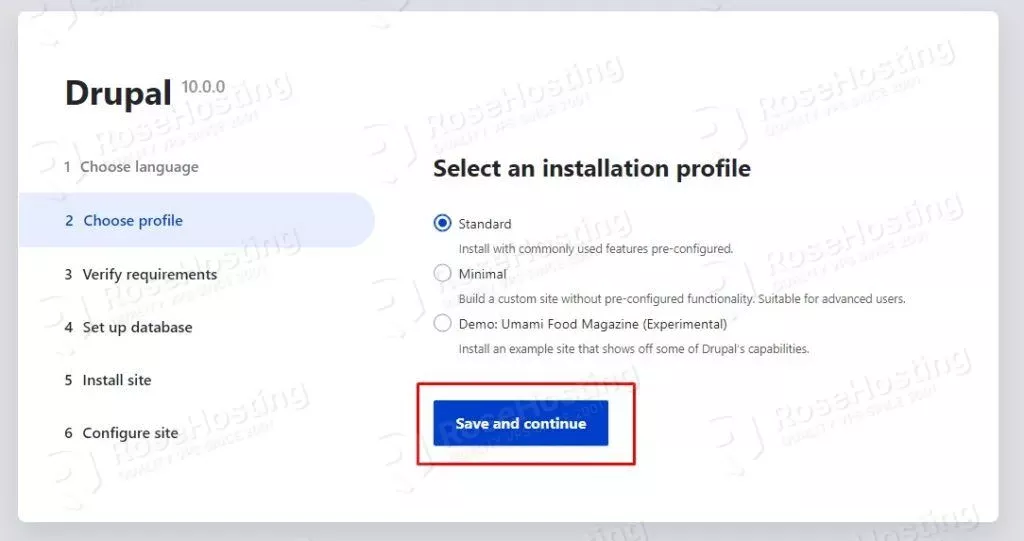
On the next window, leave the standard installation setup and click on Save and continue.
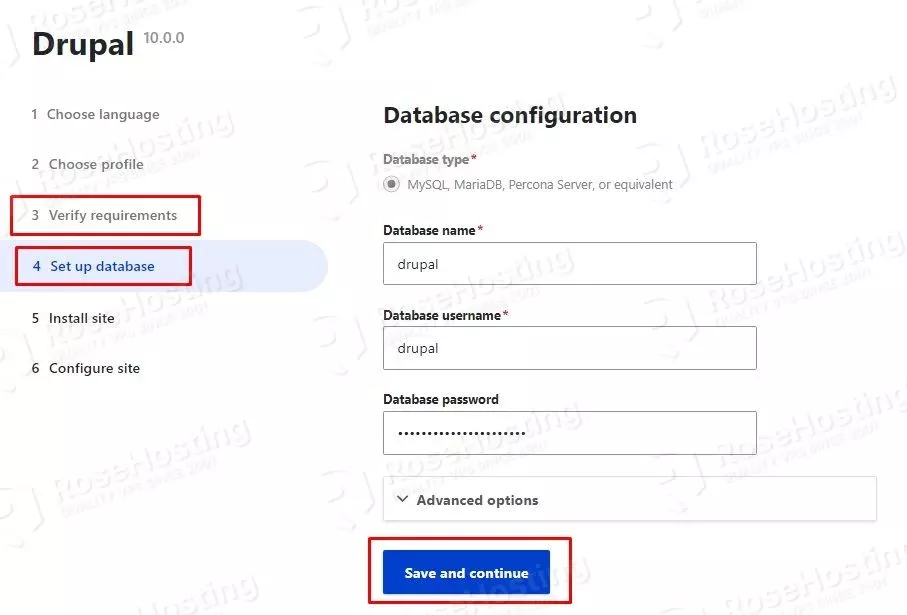
Since we installed all required dependencies, the third section will be skipped, and the user will be redirected to the database section. In this section, enter the Drupal database, user, and password you set in Step 3.
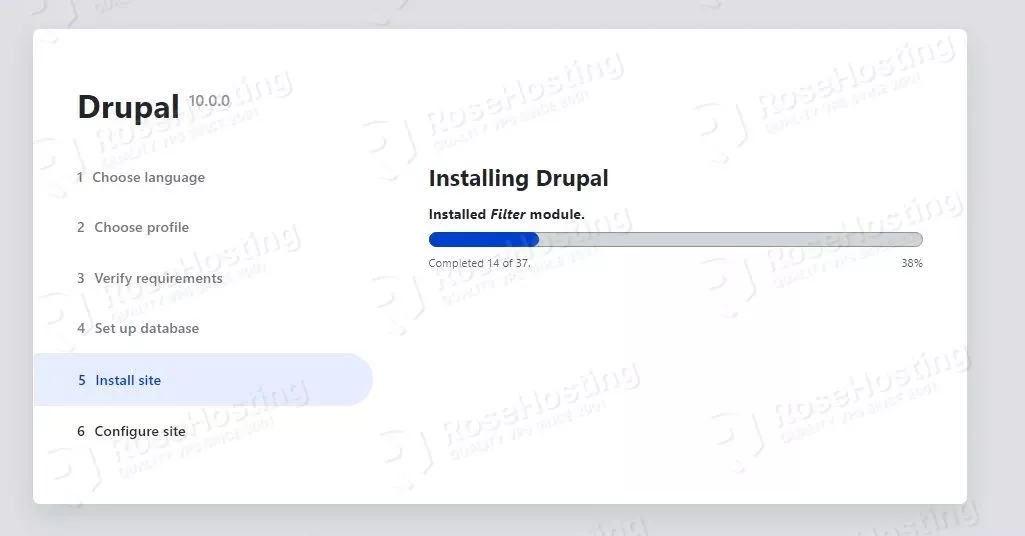
Once the database setup is completed, the installation will start:
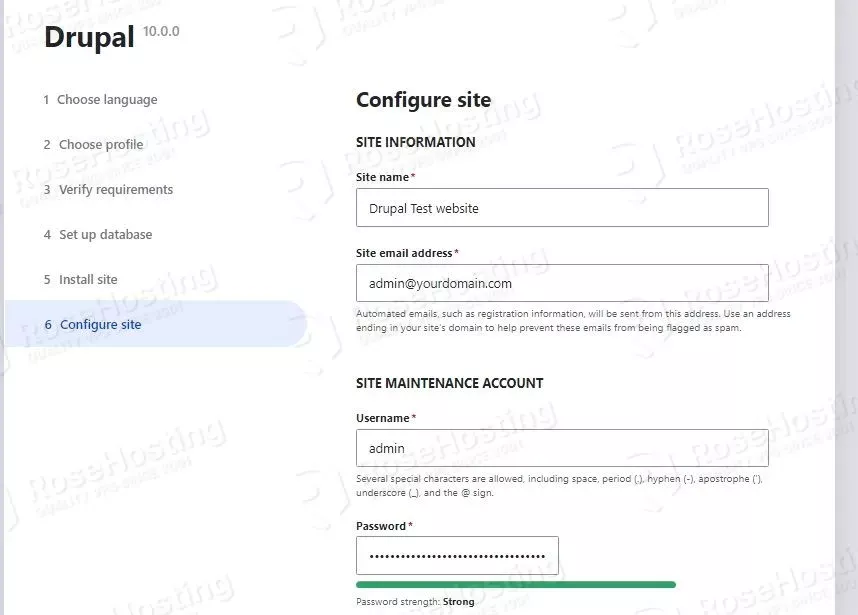
After successful installation, we need to add the website name, email, admin user, and password.
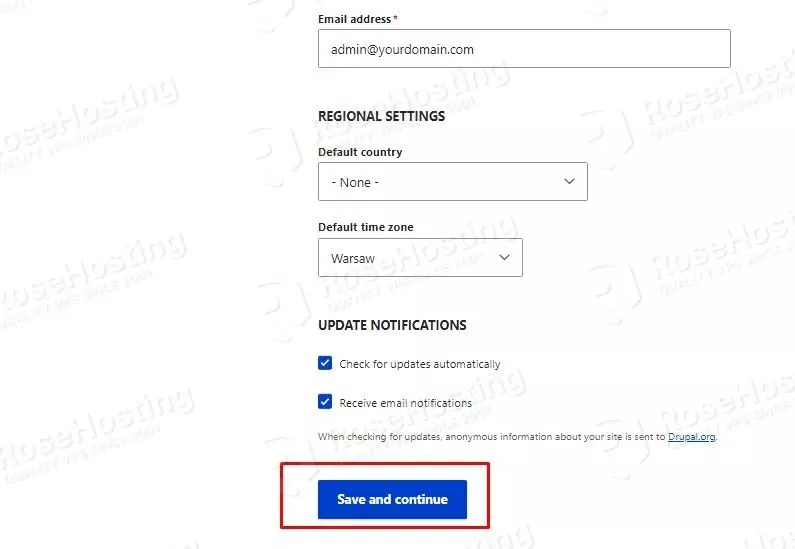
Once this is done, click on Save and continue.
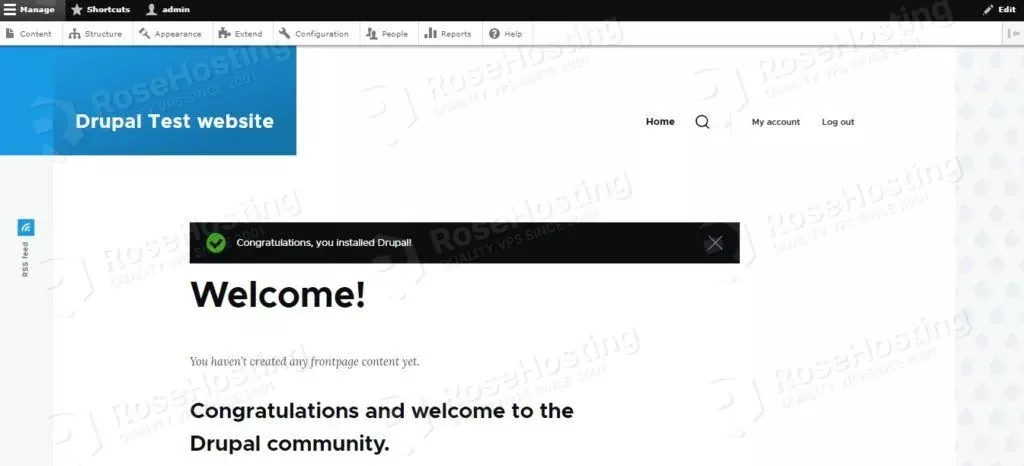
Drupal will automatically sign you into the admin dashboard.
That’s it. You successfully installed and configured the latest version of Drupal 10 on Debian 11 OS. If you find this setup difficult, please get in touch with our technical support. We are available 24/7 and will help you with your Drupal configuration. You just need to sign up for one of our NVMe VPS plans and submit a support ticket. We are waiting for you!
If you liked this post about installing Drupal on Debian 11, please share it with your friends on social networks or simply leave a reply below.